Knowledge Center Fundamental Analysis
Stock Market
Utilizing Rho in Options Trading
Among the primary Greeks utilized by options traders, Rho holds the least significance and is rarely employed. This metric gauges the theoretical alteration in an option's price in response to shifts in interest rates. Its limited importance stems from infrequent interest rate fluctuations, which typically have only a minor impact on options pricing. Nonetheless, grasping the concept of rho trading and its relevance in options trading is beneficial, and we offer a succinct overview below.
Definition Of Rho
Rho quantifies the pace at which the value of a derivative alters concerning a shift in the risk-free interest rate. Typically, it assesses the degree of an option's or options portfolio's responsiveness to fluctuations in interest rates.
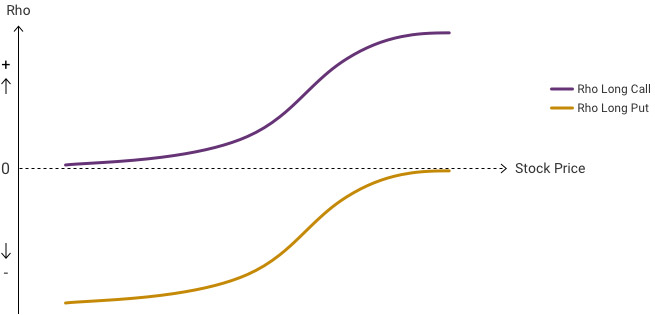
Rho is positive for long calls (the right to buy) and rises with the stock price.
Rho is negative for long puts (the right to sell) and tends toward zero as the stock price increases.
Short puts (which represent the obligation to buy) typically have a positive rho, while short calls (representing the obligation to sell) tend to have a negative rho.
Characteristics of Rho
-
Rho can take on either a positive or negative value.
-
An option with a positive rho value is expected to increase in price when interest rates rise and decrease when interest rates fall, assuming all other factors remain constant.
-
For instance, an option with a rho value of 0.01 will see its price rise by Rs. 0.01 for each percentage point increase in interest rates and decrease by Rs. 0.01 for each percentage point decrease in interest rates. Conversely, options with negative rho values behave oppositely.
-
Calls typically exhibit positive rho values, while puts tend to have negative rho values.
-
Rho values are generally higher for options with a longer time until expiration and diminish as the expiration date approaches. This is because options have less extrinsic value as they near expiration, leading to minimal impact from interest rate changes.
-
Even at its highest, rho's effect on price is typically marginal, especially for options with extensive time until expiration.
Putting Rho into Practice
-
Rho is generally not a significant factor in most options trading strategies, except during periods of dramatic interest rate changes.
-
Interest rates affect the cost of calls due to the carrying cost associated with owning financial instruments, including the potential interest cost of borrowing money.
-
As interest rates rise, the cost of calls increases because the higher carrying cost of owning the underlying security is reflected in the call prices.
-
Higher interest rates make calls more appealing to investors, as the cost savings between buying calls and owning the underlying security become more relevant.
-
Overall, while Rho is a factor in options pricing, it is often overshadowed by other Greek values such as delta, gamma, theta, and vega, which have a more significant impact on trading decisions.
Nutshell
-
Rho, among the Greeks used by options traders, is of minor significance and infrequently employed due to its limited impact.
-
Rho in stock market measures the theoretical change in an option's price in response to shifts in interest rates, but its importance is diminished by the infrequency of interest rate fluctuations.
-
rho in options can be positive for long calls, negative for long puts, and varies based on stock price changes.
-
Rho values are generally higher for options with longer expiration times and diminish as expiration approaches due to decreased extrinsic value.
-
In options trading, Rho's impact is minor compared to other Greeks like delta, gamma, theta, and vega, which have more significant effects on trading decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
How does Rho affect options?
Rho, a component of options trading Greeks, affects the pricing and behavior of options contracts. It is positive for long calls and short puts, while negative for long puts and short calls.
-
What does the rho strategy entail?
The rho strategy aims to measure how an option's price responds to a 1% shift in the underlying interest rate. Consequently, after a 1% rise or fall in the underlying interest rate, the price of an options contract would be adjusted based on its rho value.
-
What does "rho" mean in trading?
In options trading, "rho" signifies the degree of sensitivity of an option's price to alterations in interest rates. Rho values can be positive or negative, determined by the position (long or short) and the type of option (call or put).
-
How do you calculate rho options?
To calculate rho for options, you use the formula: ρ = K * t * e−r*t * N(d2), where K is the option strike price, t is the time to the option's expiry, r is the risk-free interest rate, and N is the normal cumulative distribution function. This formula incorporates various factors including the spot price (S), standard deviation (σ), and d2, which is a function of S, K, r, σ, and t.
-
Why is rho positive for calls?
Rho tends to be positive for calls due to the impact of interest rate changes on options pricing. When interest rates rise, the value of long options, such as calls, typically increases, while the value of short options, like puts, decreases. Consequently, long calls and short puts exhibit a positive rho, whereas long puts and short calls demonstrate a negative rho.
