Knowledge Center Fundamental Analysis
Trader guide
What is Stop Loss and How to Use It
Overview
Stock market trading can be complicated if the investor is not alert to the strategies to reduce the losses. The price of the shares may not always go in a favourable direction for an investor. The price may either increase or decrease. But an investor can use the stop loss option to avoid loss.
Stop Loss in the Stock Market
Stop Loss in the share market is setting up a price level by a trader to limit his potential loss on a trade. When the share price of the trade reaches the stop loss price level, stop loss order will be executed and automatically the trade will close its position to prevent further losses.
Stop Loss Order in Share Market
A stop-loss order is given to the brokerage house as a margin for avoiding heavy loss. When the investor wants to buy or sell the shares and the stop-loss order is executed, it is the right time to make the trade order. The trade order is executed when the price reaches the predetermined level while trading. The broker can place this automatic order on behalf of the investor.
An example can make it easy to understand the concept if an investor has bought a share of a company named XYZ Ltd at Rs.100 per share and presents the share price at Rs.200 per share. An investor can decide to hold the claim when the price increases and the unrealized profits. To be on the safer side, the investor requests the broker to sell the shares if the price reaches Rs.150, as the investor may be able to decide this is a bearable loss.
How To Use Stop Loss In Intraday Trading
An investor has bought a share of a company named HDFC Bank Ltd at Rs.1442.55 per share and market price of the share is at Rs.1450 per share. An investor can decide whether to hold the share when the price increases or the investor can request the broker to sell the shares if the price reaches Rs.1430, which the investor decides as a bearable loss.
The stop loss is more advantageous for the investor who cannot keep on watching the stock daily. This stands as a reminder to avoid loss. But when there is a disadvantage in stop-loss order, the price may again increase after a while; by selling the share, the investor cannot be able to enjoy the profits of the hike in price.
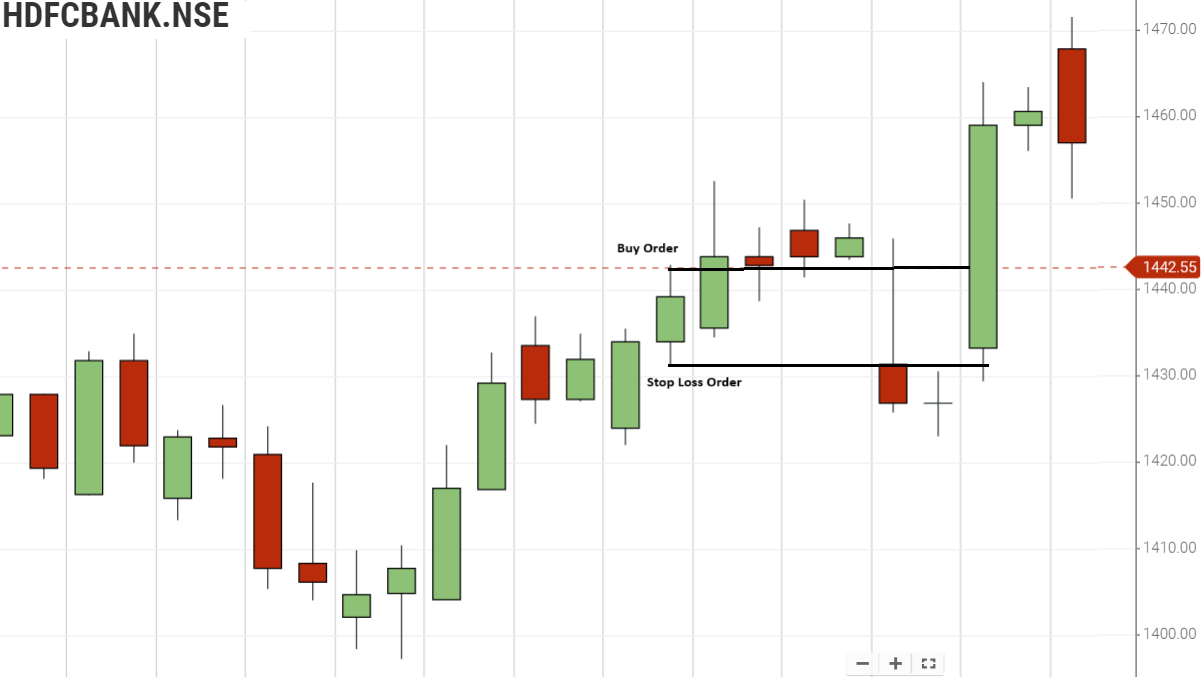
When To Use the Stop Loss Order?
The Stop Loss order is a big way for a trader to manage his intraday exposure in the market.
Let us say that a trader wants to buy HDFC Bank Limited at Rs.1442.55 because he expects the price to rise to Rs.1460 quickly. But he does not want to take an unnecessary risk, and hence he wants to exit the trade (sell his shares) in HDFC Bank Limited if the price drops below Rs. 1430.
For example, He first buys 100 shares at Rs.1442.55; then, to protect himself against an unexpected movement and limit his losses, he would place a stop-loss sell order for 100 shares of HDFC Bank Limited. With a trigger price of Rs 1430. He would choose to sell with a limit price of his choice (or) at the market price.
So, if the shares of HDFC Bank Ltd. drop to trade at Rs.1430, his order is immediately triggered and pushed into the queue for execution.
This similar process is applied in the case of short positions.
Frequently Asked Questions
How To Use Disclosed Quantity?
The system provides a facility for entering orders with quantity trade conditions. Disclosed Quantity order allows the member to reveal only a part of the order quantity to the market display. Disclosed Quantity must not be less than 10% of the Order Quantity and, at the same time, should not be greater than (or) equal to the Order Quantity.
How To Put Stop Loss In Option Trading?
To put a stop loss in options trading, first, determine the stop loss price based on your risk tolerance. Then, place a stop loss order with your broker specifying the option contract, stop price, and order type (e.g., stop loss market order). Ensure the order is valid for the trading session.
Advantages of Stop Loss Order in Trading?
-
Risk Management: Helps limit potential losses by automatically closing a position at a predetermined price.
-
Emotional Control: Prevents emotional decision-making by enforcing discipline in adhering to trading strategies.
-
Time Efficiency: Saves time by executing trades automatically, especially in volatile markets.
-
Protects Gains: Can also be used to protect profits by adjusting the stop-loss price as the trade moves in your favour.
Disadvantages of Stop Loss Order In Trading?
-
Triggered by Volatility: In volatile markets, stop-loss orders can be triggered by temporary price fluctuations, leading to selling at a loss.
-
Market Gaps: During after-hours trading or due to significant news events, prices can gap past the stop-loss level, resulting in a larger loss than anticipated.
-
Whipsawing: In choppy markets, frequent price swings can trigger stop-loss orders, leading to multiple small losses.
-
Manipulation Risk: Stop-loss orders can be targeted by market manipulators to trigger selling pressure, causing prices to drop further.
How can I set an effective stop-loss level?
Consider your risk tolerance, the volatility of the security, and technical analysis factors when setting a stop-loss level. A common approach is to set it below support levels or key moving averages.
Can stop-loss orders be used in different types of trading?
Yes, stop-loss orders can be used in various trading styles, including intraday trading, swing trading, and long-term investing, to manage risk and protect gains.
